Ppfs drawing calculating opportunity costs and allowing for
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
In today’s world, economics is vital for making informed decisions. One of the essential concepts in economics is the production possibilities frontier (PPF). The PPF is an essential tool that helps economists to evaluate the maximum output that can be achieved from limited resources. In this article, you will learn how to draw a PPF, an essential skill for any student of economics.
For many students, drawing a PPF can be a daunting task. They may be unsure of how to start, what data to use or what to include. These uncertainties can lead to confusion, frustration, and ultimately giving up on learning the concept. But with the right guidance and approach, learning to draw a PPF can be simpler than you thought.
The first step is to determine the data you’ll use for your PPF. In most cases, two products or goods are used. For instance, if you are asked to draw a PPF for maize and beans, your data will include the quantity of maize and beans that can be produced. We can use the graph to illustrate the maximum combinations of maize and beans that can be produced using the available resources
To draw a PPF, you have first to identify the data you will use. Once you have the data, you can plot it on a graph. In this context, you will plot the maximum units of maize against the maximum units of beans. The plotted graph will help visualize the maximum combination of maize and beans that can be produced with the available resources.
Personal Experience Drawing a PPF
During my Economics class, I struggled to understand how to draw a PPF. However, with the assistance of my lecturer, I learned that drawing PPF mainly involves identifying the data and plotting on a graph. The graph should have two products or goods, and we should plot them against each other.
Drawing a PPF for a specific scenario
Let’s take an example where we have two products that are computers and mobile phones. Suppose we have the following data, stating the maximum units of computers and mobile phones that a company can produce with its available resources.
The table shows data for the maximum production of computers and mobile.
 With the data available, we can plot it on a graph to draw a PPF. The horizontal axis represents computers, and the vertical axis represents mobile phones.
With the data available, we can plot it on a graph to draw a PPF. The horizontal axis represents computers, and the vertical axis represents mobile phones.
From the graph above, we can see that the company can produce a maximum of 600 computers and 300 mobile phones. The PPF curve shows the maximum production possibility frontier for both goods, and any point located inside the frontier indicates that resources are being underutilized. On the other hand, any point located outside the curve shows that resources are scarce and cannot produce at that level.
Calculating opportunity costs
In economics, opportunity cost refers to the value of what you give up by choosing one alternative over another. In the context of drawing a PPF, it is the value of the foregone good when choosing to produce more of the other good. Therefore, the opportunity cost is the slope of the PPF curve. The slope represents the rate of transformation between the two products.
Factors that cause a shift in the PPF curve
A change in resources or technology can cause a shift in the static PPF curve. This shift leads to an increase in the maximum output possibilities of the two goods. Factors such as political stability, new machines, and improved technology increase the available resources, thereby shifting the static PPF curve outwards.
Personal Experience: Understanding the Factors affecting the Shift of PPF
During my economics class, my lecturer explained the concept of static PPF and the factors that can lead to shifting of the curve. I understood that the shift in the PPF curve indicates an increase in the maximum possibility of production for the two goods. Such factors include new technology or improving political stability.
Question and Answer
1. What is the PPF?
The PPF is an essential tool that helps economists to evaluate the maximum output that can be achieved from limited resources.
2. How do you draw a PPF?
To draw a PPF, you have to identify the data you will use. Once you have the data, you can plot it on a graph. The graph should have two products or goods, and we should plot them against each other.
3. What is Opportunity Cost?
In economics, opportunity cost refers to the value of what you give up by choosing one alternative over another. In the context of drawing a PPF, it is the value of the foregone good when choosing to produce more of the other good.
4. How does the PPF curve change?
A change in resources or technology can cause a shift in the static PPF curve. This shift leads to an increase in the maximum output possibilities of the two goods. Factors such as political stability, new machines, and improved technology increase the available resources, thereby shifting the static PPF curve outwards.
Conclusion of How to Draw a PPF
Understanding how to draw a production possibility frontier is fundamental to economics. The PPF helps in understanding the combinations of goods and services that are possible based on available resources. It helps to identify the opportunity cost of choosing one alternative over the other. By following the steps outlined here, anyone can master the skill of drawing a PPF and make informed decisions based on economic principles.
Gallery
Drawing A Joint Production Possibility Frontier (PPF / PPC) - YouTube

Photo Credit by: bing.com / ppf production frontier possibility joint ppc
😀 How To Make A Production Possibilities Curve In Excel. How To Make A
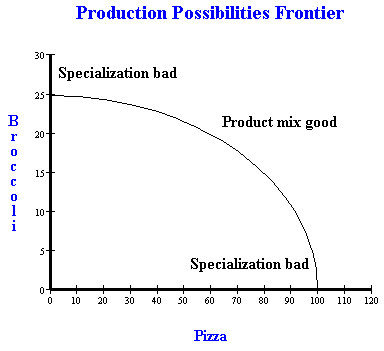
Photo Credit by: bing.com /
How To Draw A PPF (production Possibility Frontier)

Photo Credit by: bing.com / draw ppf production possibility frontier graph cost opportunity chart economics diagram table constant own trade off freeeconhelp goods board each
PPFs: Drawing, Calculating Opportunity Costs, And Allowing For
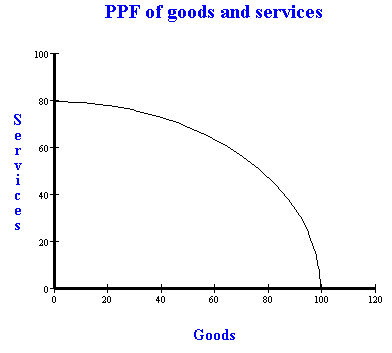
Photo Credit by: bing.com / ppf opportunity cost drawing graph economics costs trade calculating goods example services good service different look data ppfs which freeeconhelp
Introduction Of The Keynesian Short-run Aggregate Supply Curve.

Photo Credit by: bing.com / ppf draw production possibility frontier economics examples goods public





