Rlc phasor fasor draw impedance sirkuit rangkaian vc
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
If you’re an electrical engineering student or a professional working with AC circuits, you’ve probably come across the term “phasor diagram”. While it may seem intimidating at first, understanding how to draw a phasor diagram is crucial for analyzing and understanding AC circuits. In this post, we’ll explore the basics of phasor diagrams and how to draw them step-by-step.
When it comes to understanding AC circuits, one of the biggest pain points is visualizing how the current and voltage in a circuit vary over time. This is where phasor diagrams come in handy. By representing the AC voltage and current as phasors, which are rotating vectors with magnitude and phase angle, we can easily analyze the behavior of the circuit without having to deal with the time-varying signals.
To draw a phasor diagram, we start by noting the phasor of the AC voltage source. The phasor will be represented as a line segment drawn from the origin of a coordinate system, and its length will represent the amplitude of the voltage. The angle between the phasor and the positive x-axis will represent the phase angle of the voltage. We then add phasors for the other elements in the circuit, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, based on their impedance values and angular frequencies. By summing up all the phasors, we get the overall phasor for the circuit, which represents the net voltage and current in the circuit.
In summary, drawing a phasor diagram involves representing AC voltage and current as phasors, adding phasors based on impedance and angular frequency, and summing up all the phasors to get the overall phasor for the circuit. By doing so, we can easily analyze the circuit’s behavior without having to deal with time-varying signals.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Draw a Phasor Diagram
When I first learned about phasor diagrams, I found them to be quite daunting. However, with practice and patience, I was able to master the technique. Follow these steps to draw a phasor diagram:
Step 1: Identify the AC voltage source and note its amplitude and phase angle.
 Step 2: Identify the impedance of each circuit element, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. Note the angular frequency of the circuit.
Step 2: Identify the impedance of each circuit element, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. Note the angular frequency of the circuit.
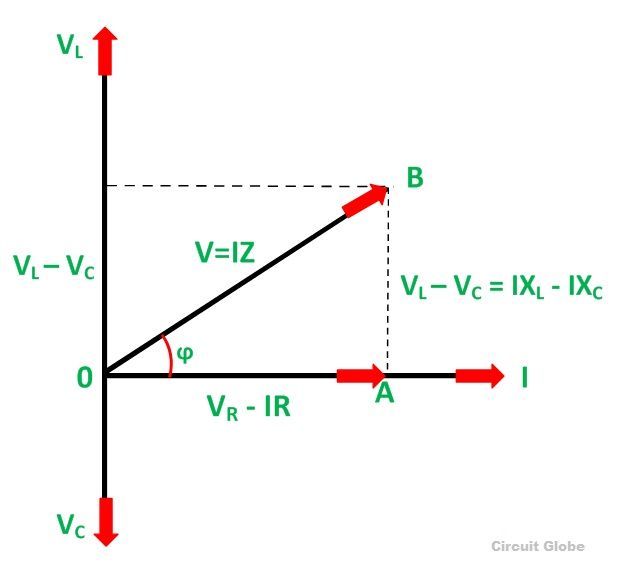 Step 3: Draw the phasor for each circuit element based on its impedance and angular frequency, with the tip of the phasor pointing in the direction of the current flow.
Step 3: Draw the phasor for each circuit element based on its impedance and angular frequency, with the tip of the phasor pointing in the direction of the current flow.
 Step 4: Add the phasors for each circuit element to get the overall phasor for the circuit.
Step 4: Add the phasors for each circuit element to get the overall phasor for the circuit.
 Tips and Tricks for Drawing Phasor Diagrams
Tips and Tricks for Drawing Phasor Diagrams
One of the best ways to learn how to draw phasor diagrams is to practice with different types of circuits. Here are some additional tips and tricks to keep in mind:
Tip #1: Use a protractor to measure the angle of each phasor accurately.
Since the angle between phasors is crucial in determining the overall behavior of the circuit, it’s essential to measure the angles accurately using a protractor.
 #### Tip #2: Use different colors for each phasor to make the diagram clearer.
#### Tip #2: Use different colors for each phasor to make the diagram clearer.
By using different colors for each phasor, you can make the diagram more organized and easier to understand.
 FAQs About Drawing Phasor Diagrams
FAQs About Drawing Phasor Diagrams
Q: What is the purpose of a phasor diagram?
A: The purpose of a phasor diagram is to simplify the analysis of AC circuits by representing the AC voltage and current as rotating phasors with magnitude and phase angle. By doing so, we can easily analyze the behavior of the circuit without having to deal with time-varying signals.
Q: Can I use phasor diagrams for DC circuits?
A: No, phasor diagrams are only applicable to AC circuits, where the voltage and current vary sinusoidally over time. DC circuits have a constant voltage and therefore do not require phasor diagrams.
Q: How do I know which direction to draw the phasor for each circuit element?
A: The direction of the phasor is based on the direction of the current flow in the circuit element. For resistors, the current flows in the same direction as the voltage drop across the resistor, so the phasor points in the direction of the voltage drop. For capacitors and inductors, the direction of the current flow depends on the phase angle.
Q: Do I need to draw the phasors to scale?
A: Yes, it’s essential to draw the phasors to scale because the length of each phasor represents the magnitude of the voltage or current in the circuit. If the phasors are not drawn to scale, the analysis of the circuit may be inaccurate.
Conclusion of How to Draw a Phasor Diagram
Learning how to draw a phasor diagram is a crucial skill for anyone working with AC circuits. By representing AC voltage and current as phasors, we can simplify the analysis of the circuit and easily understand its behavior. To draw a phasor diagram, we need to identify the AC voltage source, note the impedance and angular frequency of each circuit element, draw the phasors for each element, and add all the phasors to get the overall phasor for the circuit. By following these steps and practicing consistently, we can master the art of phasor diagrams.
Gallery
What Is RLC Series Circuit? - Phasor Diagram & Impedance Triangle

Photo Credit by: bing.com / rlc phasor fasor draw impedance sirkuit rangkaian vc
How To Draw A Phasor Diagram - Drivenheisenberg

Photo Credit by: bing.com / draw phasor diagram tikz angles tex
Draw Phasor Diagram Online

Photo Credit by: bing.com / diagram phasor draw shown circuit below paper graph engineering use step determine phasors select change menu create asap answer please
Draw Phasor Diagram Online

Photo Credit by: bing.com / diagram phasor draw drawing axis latex tikz angles horizontal reference current take
How To Draw A Phasor Diagram – Learn.org.au

Photo Credit by: bing.com / phasor diagram draw ac learn au week circuits map
 FAQs About Drawing Phasor Diagrams
FAQs About Drawing Phasor Diagrams




